Everything You've Ever Wanted to Know About Digitalization
Published on 12/21/2020 by Yahong Zhang
What is digitalization?
Digitalization is described by Gartner as “the use of digital technologies to change a business model and provide new revenue and value-producing opportunities; it is the process of moving to a digital business.”
For the past decades, businesses have been evolving towards digitalization and trying to shift into a more technological approach that adopts digital tools in everyday tasks, at both individual and organizational levels, to have more accessible and transparent data, faster processes and higher productivity.
Companies are embracing Digital Transformation due to static traditional approaches
Digitalization quickly gave birth to a related term, “Digital Transformation/ DX”, which refers to how companies prioritize IT modernization and digital optimization to create better business models that help rediscover and satisfy the raw customer needs.
It might sound like a very complicated concept, but Digital Transformation is now a process that every modern company has initiated or has already implemented.
A simplified 3D visualization and configuration demonstration provided by luxury brand Lolo Chatenay and tech startup Hapticmedia.
As TechPro Research shows, 70% of companies either have a digital transformation strategy in place or are working on one, while the IDG Digital Business research showes that 44% of organizations had fully adopted a digital-first business approach.
For those who are unsure about digitalization, warnings are everywhere
In the XXIst century, digitalization becomes a must for any company that wants to remain competitive in the market. As the COVID-19 crisis has proven, slow responses to digitalization may break an organization, no matter how big it is.
Examples include Neiman Marcus, Bergdorf Goodman, Mytheresa, Horchow and Last Call.
Increasing interests from consumers in digital experiences and online content.
One reason why digitalization is extremely important for businesses is that consumers are consistently developing new shopping patterns and demands.
According to the report Digital 2020 by WeareSocial and Hootsuite, more than 4.54 billion people (around 60% of the Globe’s population) are currently online, while 5.19 billion use mobile phones. Just in 2019, 298 million people mainly from developing economies, have joined the world wide web.
The average internet user now spends 6 hours and 43 minutes online each day, browsing websites, social media, apps, enjoying the benefits of online shopping and streaming services and so on.
During the quarantine too, digital consumption may increase to 60% or more, according to Nielsen research. Even in Hong Kong, which is mostly a brick-and-mortar market, consumers quickly adjusted and downloaded e-commerce apps.
Moreover in Asia, the region that was firstly struck by COVID-19, social media quickly became platforms for sharing news about COVID-19 cases and related regulations.
Increasing investments from enterprises in Digital Transformation
Now, enterprises worldwide are making investments in the digital transformation of business models, customer and channel engagement, products and services, economic models and operations.
International Data Corporation forecasts that digital technology investment will grow across all sectors, ranging between 15% and 20%, while the overall digital transformation spending was already over $1 trillion in 2018.
What are the elements of a successful digital transformation journey?
Pillar #1: A digital strategy and a new business model to innovate and capture value
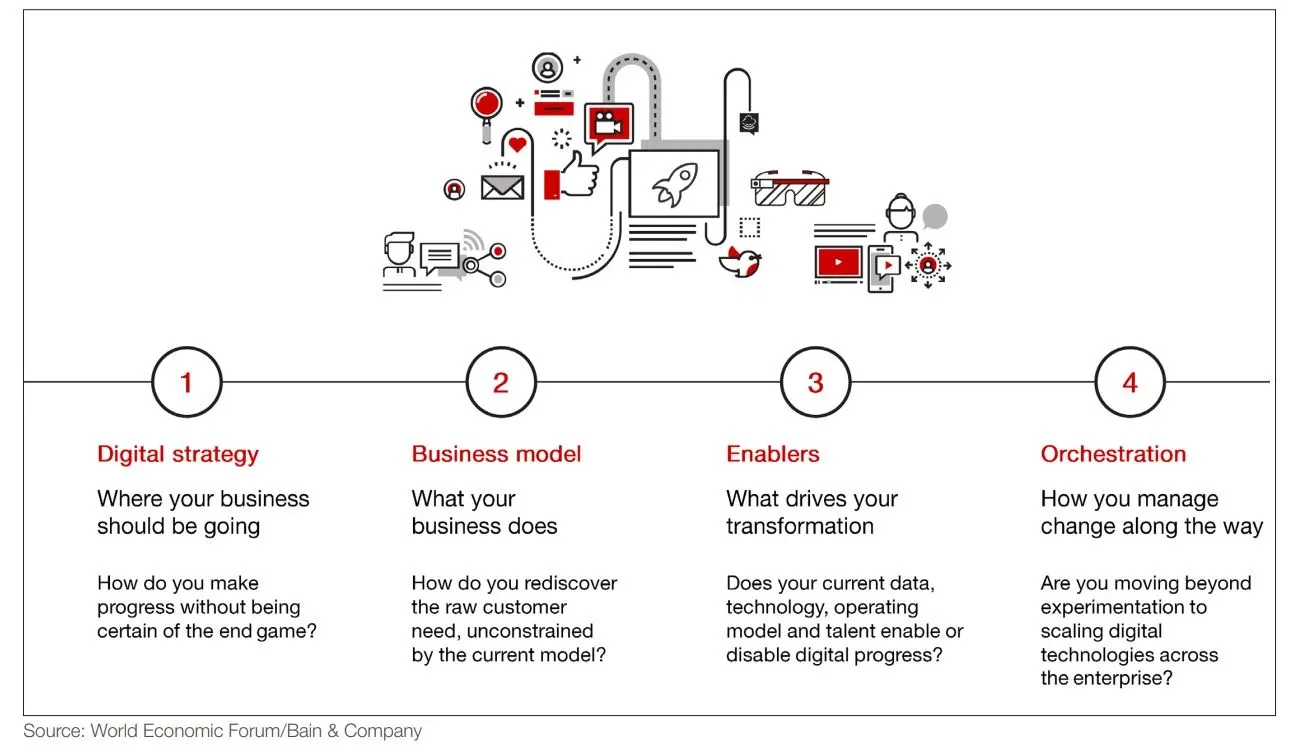 Source: The Digital Enterprise Moving from experimentation to transformation.
Source: The Digital Enterprise Moving from experimentation to transformation.
According to a research by The World Economic Forum in collaboration with Bain & Company, traditional approaches to today’s business and operational objectives are too linear and static.
Members of the working group have agreed that companies need aspirational views of the future to set a direction, as well as an increased flexibility to pivot and evolve. This means that adaptability, a high speed of reaction and simultaneous development are of the essence and these may be achieved through a digital strategy as well as digital tools that simplify decision-making, communications, implementation and flows.
Strategy is foundational, but it requires more to be taken to market. That's what a business model serve. It describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value, in economic, social, cultural or other contexts.
A business model built for a digital enterprise is also required and should include a few essential elements including customer and channel engagement, products and services, operations, culture and talents.
Pillar #2: A more engaging digital customer experience
In spite of efforts to invest in technology for a better experience, big retail brands like Neiman Marcus have been struggling to adopt digitalization. In 2017, the company was facing difficulties in implementing a cross-channel merchandising system, which led to a significant loss worth $55 - $65 million.
Digital platforms have proven very efficient for both brands and consumers.
For example, online luxury sales is becoming increasingly popular in the past years, as baskets have grown both in values and in numbers, contributing to 39% of overall luxury sales growth.
It is difficult to talk about eCommerce without China, which has been taking a leading role in the retail transformation. With online consumption consistently increasing and 64% of e-commerce adoption among Chinese consumers, the Chinese e-shopping retail market has 650 million users and was assessed at $1.5 trillion in 2019, making it larger than the next 10 markets combined.
Consumers need an engaging and personalized shopping experience, as well as customized products tailored to their unique tastes.
Brands like Guerlain have doubled their conversions by offering beauty fans the opportunity to create their own lipstick on DTC channels. The 3D configurator designed by Hapticmedia enables make-up fans to actually see how the product would look before ordering it.
The new shopping experience: less direct contact and more digital tools and technologies.
Scientists say we should learn to live with COVID-19 over the next few months or years, let alone new crisis. This means that direct human interactions will be limited and companies have to deploy digital tools to communicate and engage with customers.
Advanced technologies like chatbots, Artificial Intelligence and big data are becoming extremely popular now, not only at handling inquiries and complaints, but also offering products recommendations and proactive suggestions.
A great example of integrating virtual try on technology into the multi channel marketing strategy can be taken from Baume, a high- end watchmaking brand.
Still, we can do more. Virtual fitting rooms, 3D product configuration, try-on technology, live streaming, immersive reality, mass customization, such technologies are now bringing new opportunities to e-commerce, making it possible for consumers to find products that best suit their tastes and demands.
Pillar #3: Offering innovative products and services in a digital era
As an increasing number of consumers are going online, they expect brands to keep up with demands and offer convenience in this digital environment. According to a report published by the National Retail Federation, 83% of consumers attribute a higher importance to convenience than 5 years ago. Moreover this attribute brings to retailers a competitive advantage, as 97% of respondents have quit a purchase, because of inconvenience.
Modernisation is creating a context for digitalization. In 2013, the sharing economy was assessed as $15 billion, significantly lower than the traditional operating model which was at $240 billion; however, by 2025 the two are expected to even out, each reaching a market value at $335 billion.
This means that demands for location-based computing, product configuration, chatbots, virtual try-on, Internet Of Things and cloud services will continue to grow and that brands will need to adjust.
Smart home adoption is also on the rise, as the International Data Corporation estimates that 1.39 billion devices will be shipped in 2023. In the West, corporations like Amazon, Google, Apple and Samsung have created large internet of things and smart-home platforms; while in China, the market is governed by big names like Baidu, Alibaba, Xiaomi. Technologies such as connected TVs, smart speakers, cleaning robots, lighting, thermostats, security systems, camera and door locks have become part of consumers’ daily lives.
Although innovation is led by big players who invest in technology, new comers are also getting involved and developing cross-compatible products and services. Innovation is on the grow. Digital evolution is thus a continuous process that is centered around consumer demands.
Pillar #4: Transforming operations, processes and systems
The way that business is done around the world is changing rapidly. This is because technology is advancing so quickly that it is making things possible that have never before.
For example, smart factories, the internet of things, robots, location detection technologies, advanced human-machine interfaces, 3D printing, augmented reality, big data, and 3D technology are reshaping the way that companies produce products and the way that customers search for, engage with, and shop for products.
All of these changes are resulting in the creation of Industry 4.0, which is marked by the digitization of manufacturing and the computerization of industry.
Impacts: high levels of automation, customization and productivity due to new technologies
The digitization and integration of vertical and horizontal value chains, of product and service offerings and of business models and customer access is ultimately fueled by the desire of companies to digitize as many components of their business as possible using breakthrough technologies such as AI, machine learning, and big data.
And the goal is to reduce dependence on human workers, increase profit margins, dramatically boost production, automate as many facets of their businesses as possible, be able to easily adapt to changing customer preferences, and to have machines adapt and learn on their own over time.
Pillar #5: Cultivating a digital culture and attracting digital talents
Digital transformation isn’t solely about technology, but very much about people and how they relate to this notion. This is why it is believed that that a strong digital culture is a key Digital Transformation driver.
To create an environment or a culture that fosters digitalization, it is essential to understand that different types of employees approach technology differently. Some are extremely passionate, some are undecided, while others are actually reluctant. Each of them needs to be guided through their own journey. A carefully crafted communication strategy in this case is supposed to be in place.
To achieve this goal, companies need to create a business relationship management structure supported by digital talents, that facilitates interactions between business units and IT departments, and develop digital capabilities among team members.
Another important aspect in developing a strong digital culture is motivating people to be open minded and to try to accept the concept of Digital Transformation, by showcasing that technology is not an objective in itself, but a means which helps professionals and companies to optimize processes and results and therefore to attain their goals.
This may be done through examples, case studies or an analytical approach to tasks.
Once employees understand that technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, Big Data and Analytics are meant to help them save time and optimize deliverables, without threatening their jobs or the working environment, they will be much more willing to adopt this digitally-savvy strategy.
Marketers are expected to act as a key driver of digital transformation
In a report To Get a Seat at the Table, Command Your Customer’s Experience by Forrester, it is showcased that CMOs are less likely to be the leaders in digital transformations, compared to their C-suite peers.
Actually, as figures show, only 23% of CMOs are involved in strategy and only 16% in execution, which is significantly less compared to technology leaders like IT managers, CIOs and CTOs, or even CEOs, COOs, CFOs and so on.
What presents as a concern is that, when digital transformation is left to CIOs or IT departments, the focus becomes more about improving efficiency and optimizing resources, less about satisfying consumer demands. In this case, an important pillar of digitalization is neglected.
As marketing is shifting towards martech, professionals in the field are expected to use digital tools to create authentic, inspiring and engaging customer moments that are carefully orchestrated and coordinated, across all channels and media.
Moreover, they need to not only streamline processes but also to generate customer satisfaction and loyalty, creating is a core competitive advantage.
And this is totally doable, as long as marketers are fully involved and take a leading role in this digitalization journey, since digital transformation is no longer a buzzword. It’s an imperative.
Resources
https://resources.idg.com/download/white-paper/2018-digital-business
https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/digitalization
https://martechtoday.com/why-marketers-need-to-help-manage-digital-transformations-231265
https://martechtoday.com/digital-transformation-is-no-longer-a-buzzword-its-an-imperative-240749
https://www.deloittedigital.com/us/en/blog-list/2019/driving-brand-loyalty-with-emotion.html
https://research.aimultiple.com/digital-transformation/
The Digital Enterprise Moving from experimentation to transformation by Bain & Company